Day 02
Pablo Gomez
How can we find help with R?
Using the ? operator:
How can we find help with R?

How can we find help with R?

How can we find help with R?

How can we find help with R?
How can we find help with R?
! WARNING: CHAT GPT CAN GIVE INCORRECT INFORMATION !
- If chat GPT does not knows something, sometimes will make up information (i.e. made up references, name of packages, libraries etc…)
- Make sure to verify the information provided by Chat GPT
How can we find help with R?

Recap from Day 01
R syntax
x <- seq(from = 5, to = 23, length.out = 10) # create a sequence of numbers
y <- seq(from = 0.1, to = 0.78, length.out = 10) # Create another sequence
mean(x*y) # Get the mean of the multiplication[1] 7.406667Objects? Operators? Functions? Arguments?
Objects:
- x
- y
Operators:
- *
- <-
Functions:
- seq()
- mean()
Arguments:
- from
- to
- lengt.out
Recap: functions for reduction
Some of the function we reviewed:
select()slice()filter()
Recap: functions for reduction
Some of the function we reviewed:
select()to select specific columnsslice()filter()
Recap: functions for reduction
Some of the function we reviewed:
select()to select specific columnsslice()to select specific rows based on positionfilter()
Recap: functions for reduction
Some of the function we reviewed:
select()to select specific columnsslice()to select specific rows based on positionfilter()to select specific rows based on a condition
Review: functions
Review: functions
Review: functions
Review: functions
Review: functions
Review: functions
Review: functions
Other function we reviewed:
count()Count rows by one or more groupsgroup_by()aggregate the data by one or more groupssummarise()applies functions to the grouped variablesleft_join()join tables based on one or more index variables
Data visualization
ggplot2
- We build our figures based on layers
- Similar syntax as dplyr
- We can combine data wrangling and visualization into a single code chunk

Instead of the %>%, in ggplot we connect pieces of code with +
ggplot2
The basic components that we need to define for a plot are the following:
- data, the data set we will use to generate the figure
- geometry, or type of graphic we will generate (i.e. histogram, bar, scatter, etc..)
- aesthetic, variables or arguments that will be used for the figure for example: location, color, size, etc..
Example
| municipality | location | Loc | date | year | captures | treated | lat | lon | trap_type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temascaltepec | San Pedro Tenayac | Cueva el Uno | 11/06/14 | 2014 | 6 | 6 | 18.03546 | -100.2095 | 1 |
| Tlatlaya | Nuevo Copaltepec | La alcantarilla | 12/05/05 | 2005 | 3 | 2 | 18.40417 | -100.2688 | 1 |
| Tlatlaya | Nuevo Copaltepec | La alcantarilla | 12/05/07 | 2007 | 30 | 29 | 18.40417 | -100.2688 | 4 |
| Tlatlaya | Nuevo Copaltepec | La alcantarilla | 12/03/09 | 2009 | 0 | 0 | 18.40417 | -100.2688 | 3 |
| Tlatlaya | Nuevo Copaltepec | La alcantarilla | 10/08/10 | 2010 | 4 | 3 | 18.40417 | -100.2688 | 1 |
Example
| year | n |
|---|---|
| 2005 | 167 |
| 2006 | 103 |
| 2007 | 249 |
| 2008 | 143 |
| 2009 | 125 |
Example

Example
Example
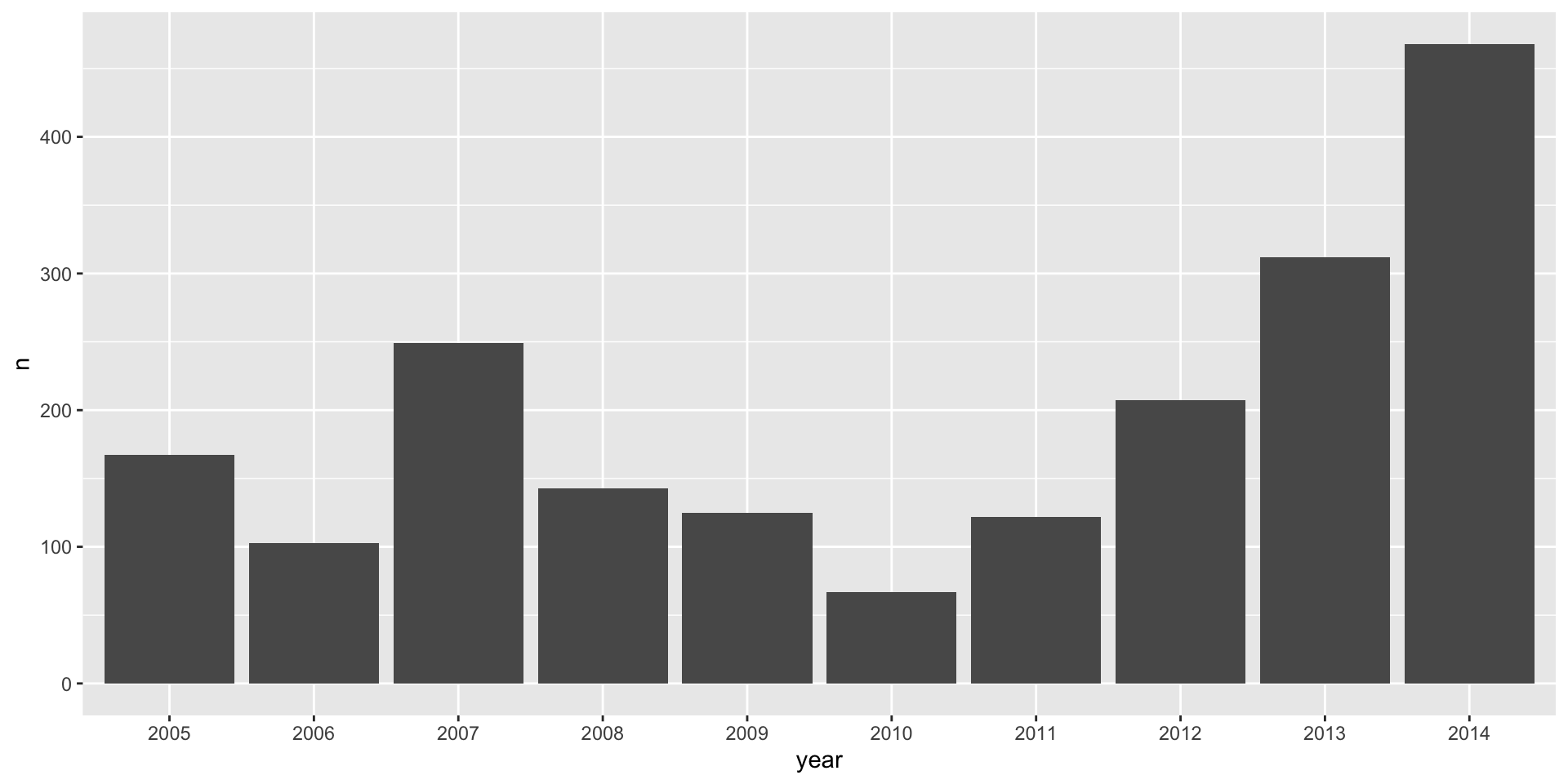
Example
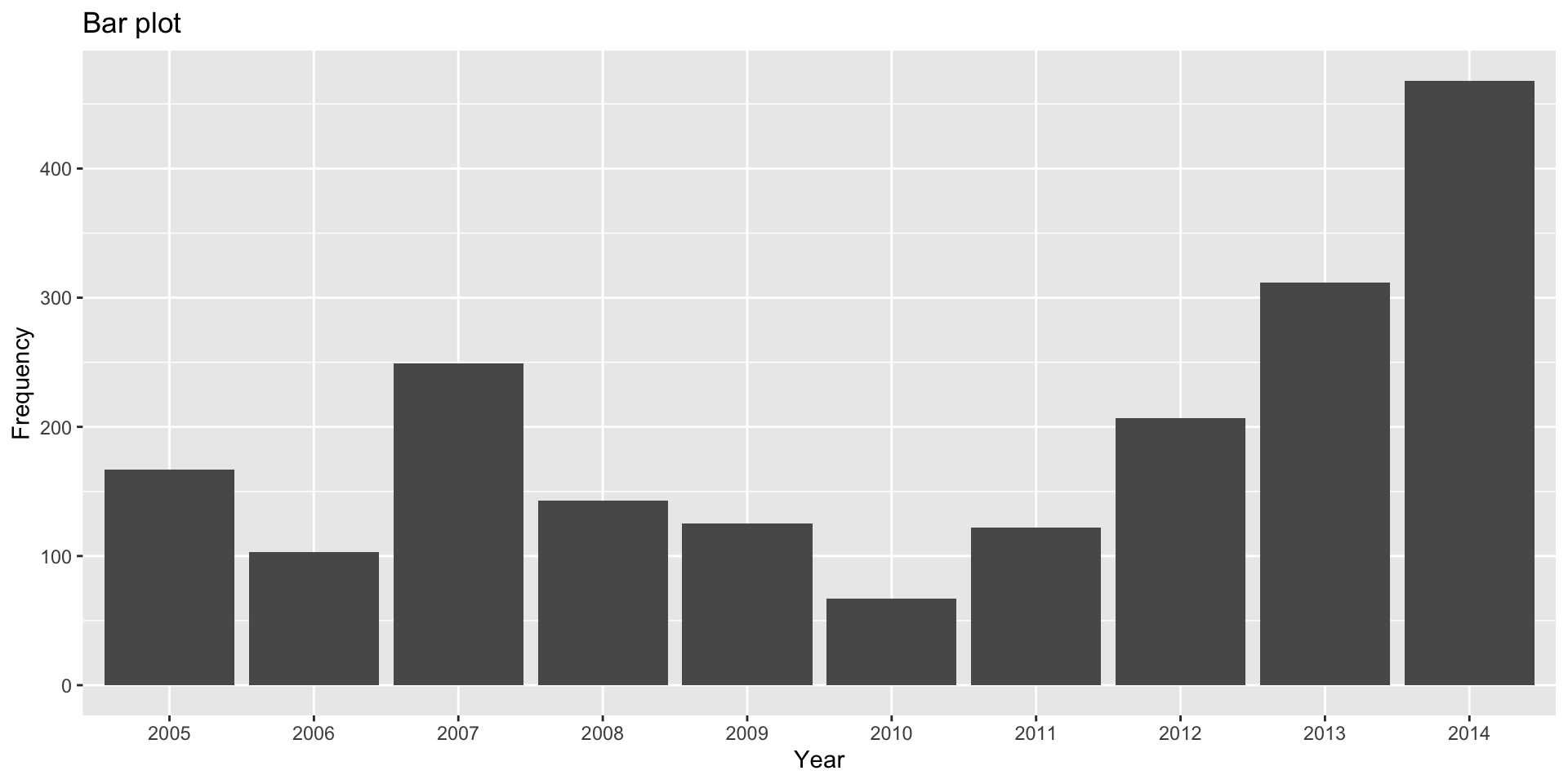
ggplot2

It’s Lab time!
Graphics in R
How can we find help with R?

Spatial Data
Spatial data formats
Vectors 
Rasters 
Spatial resolution
Vectors
Point
Lines
Polygon
Spatial data in R
library(sf)
# Loading the spatial data from the package
MxSp <- st_read(system.file("data/MxShp.shp", package = "STNet")) Reading layer `MxShp' from data source
`/Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.2-arm64/Resources/library/STNet/data/MxShp.shp'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 2471 features and 6 fields
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 1058748 ymin: 319149.1 xmax: 4082958 ymax: 2349605
Projected CRS: MEXICO_ITRF_2008_LCCSpatial data in R
Spatial data in R
Simple feature collection with 6 features and 6 fields
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: -100.5848 ymin: 16.88094 xmax: -98.218 ymax: 18.35471
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
CVEGEO CVE_ENT CVE_MUN NOMGEO AREA_LCC ID
1 12067 12 067 Tlapehuala 284.696 12067
2 12043 12 043 Metlatónoc 584.023 12043
3 12081 12 081 Iliatenco 235.682 12081
4 12066 12 066 Tlapa de Comonfort 609.030 12066
5 12078 12 078 Cochoapa el Grande 638.160 12078
6 12079 12 079 José Joaquín de Herrera 131.977 12079
geometry
1 MULTIPOLYGON (((-100.3237 1...
2 MULTIPOLYGON (((-98.26956 1...
3 MULTIPOLYGON (((-98.57511 1...
4 MULTIPOLYGON (((-98.5618 17...
5 MULTIPOLYGON (((-98.28944 1...
6 MULTIPOLYGON (((-98.95271 1...Spatial data in R
The output shows:
geometry type: The type of shapefile (either point data, lines or polygons).
dimensionDimensions used in the data.
Bounding box: The extent of our data.
CRS: The coordinate reference system.
- And the first 10 features.
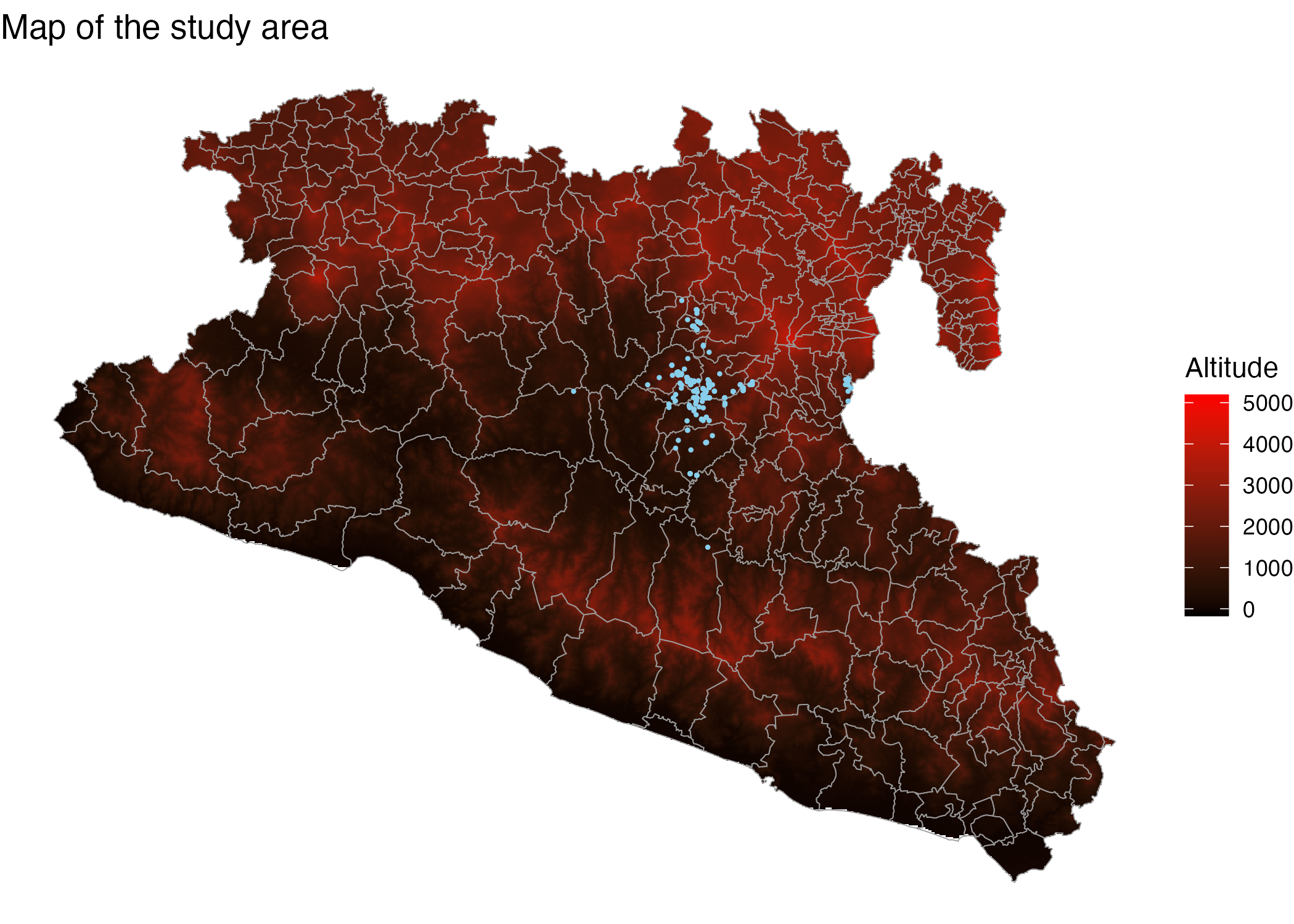
Maps
ggplot() + # create the empty canvas
geom_stars(data = Mxst) + # add raster layer
geom_sf(data = Area, fill = NA, col = 'grey60') + # add polygon layer
geom_sf(data = capturesSp, cex = 0.3, col = 'skyblue') + # add point layer
theme_void() + # theme for the figure
scale_fill_gradient(low = 'black', high = 'red', na.value = NA) + # color for the gradient
labs(title = 'Map of the study area', fill = 'Altitude') # labels for the figure